More Cryptographic Concepts for Developers
...
Digital Certificates, the X.509 Standard and PKI
...
https://cryptography.io/en/latest/x509/
Transport Layer Security (TLS) and SSL
...
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security
A cipher suite is a set of algorithms that help secure a network connection that uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) or its now-deprecated predecessor Secure Socket Layer (SSL). The set of algorithms that cipher suites usually contain include: a key exchange algorithm, a symmetric encryption algorithm, and a message authentication code (MAC) algorithm.
External Authentication and OAuth
...
Two-Factor Authentication and One-Time Passwords
Multi-Factor authentication adds additional layers of identity authentication. Usually, those factors should be added to some of the following categories:
- What I know
- What I have
- What I am
Two-Factor Authentication requires two of those three categories to be implemented. The most common case of Two-Factor Authentication is a user password and a device on which will be sent/generate one-time-password. To generate a one-time-password (OTP) the HMAC-based One-time Password algorithm is used.
HMAC-based One-time Password (HOTP)
The HOTP algorithm is based on HMAC and provides a symmetric generation of human-readable passwords, each used for only one authentication attempt. The key parameter of HTOP is a secret which has to be exchanged between the parties in advance:
HTOP(has_function, secret, value_length) -> htop
htop.generate() -> auth_code
htop.validate(auth_code) -> true/false
The hash_func can be any cryptographic hash function. The secret is the arbitrary byte string which must be shared between the parties and kept private. value_length defines the auth_code length.
Counter-based One-Time Password algorithm (COTP)
In the COTP scenario the HTOP function contains an internal counter. In order for parties to successfully authenticate each other they have to keep their counters in sync. Each time HOTP is requested to generate an auth_code the counter increments.
Time-based One-Time Password Algorithm (TOTP)
Time-based One-Time Password Algorithm (TOTP) is an extension of COTP, where the counter is the current time, defined as Unix time. The time-interval is another parameter used for the generation of TOTP, which defines a period of time of which a given authentication code will be valid.
htop_counter = (current_time - initial_time) / time_interval
For TOTP to work correctly both parties need to have synchronized clocks with minimal verification time-step window (delay based on user's input, network latency, and clock time deviation).
otp = TOTP(hash_function(secret), htop_counter)
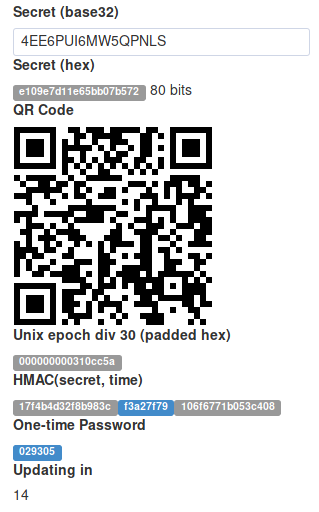
Time-based One-Time Password in Practice
A popular use case of Two-Factor Authentication is the Google Authenticator. A server generates a secret and shares it as a QR code with the client. The client scan and store the secret in the Google Authenticator application on a phone. After that, the server and the phone start to generate the same one-time passwords.
An example of a web-based JavaScript example for using and testing TOTP:
Infected Cryptosystems and Crypto Backdoors
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kleptography
Other Cryptographic Concepts and Standards
Just to mention, the practical cryptography is endless. This is a list of crypto concepts, algorithm, protocols and standards that we will not going to explain in this book, but you can read about them from the provided links:
Kerberos - ...
IPsec - ...
WiFi cryptography standards - ...
PGP - ...
S/MIME - ...
JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
Object Identifiers (OID) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Object_identifier, e.g. the algorithm "SHA-256" has OID "2.16.840.1.101.3.4.2.1".
Cryptography Best Practices: https://gist.github.com/atoponce/07d8d4c833873be2f68c34f9afc5a78a