Spring MVC 3.1新特性 生产者、消费者请求限定 —— 第六章 注解式控制器详解——跟着开涛学SpringMVC
6.6.5、生产者、消费者限定
6.6.5.1、基本概念
首先让我们看一下通过HTTP协议传输的媒体类型及如何表示媒体类型:
一、Media Type:
互联网媒体类型,一般就是我们所说的MIME类型,用来确定请求的内容类型或响应的内容类型。
写道媒体类型格式:type/subtype(;parameter)? type主类型,任意的字符串,如text,如果是号代表所有; subtype 子类型,任意的字符串,如html,如果是号代表所有; parameter 可选,一些参数,如Accept请求头的q参数, Content-Type的 charset参数。
详见http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2616#section-3.7
常见媒体类型:
text/html : HTML格式 text/plain :纯文本格式 text/xml :XML格式
image/gif :gif图片格式 image/jpeg :jpg图片格式 image/png:png图片格式
application/x-www-form-urlencoded : <form encType=””>中默认的encType,form表单数据被编码为key/value格式发送到服务器(表单默认的提交数据的格式)。
multipart/form-data : 当你需要在表单中进行文件上传时,就需要使用该格式;
application/xhtml+xml :XHTML格式 application/xml : XML数据格式
application/atom+xml :Atom XML聚合格式 application/json : JSON数据格式
application/pdf :pdf格式 application/msword : Word文档格式
application/octet-stream : 二进制流数据(如常见的文件下载)。
在如tomcat服务器的 “conf/web.xml”中指定了扩展名到媒体类型的映射,在此我们可以看到服务器支持的媒体类型。
二、Content-Type:内容类型,即请求/响应的内容区数据的媒体类型;
2.1、请求头的内容类型,表示发送到服务器的内容数据的媒体类型;
request中设置请求头“Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded”表示请求的数据为key/value数据;
(1、控制器cn.javass.chapter6.web.controller.consumesproduces.contenttype.RequestContentTypeController
@RequestMapping(value = "/ContentType", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String showForm() throws IOException {
//form表单,使用application/x-www-form-urlencoded编码方式提交表单
return "consumesproduces/Content-Type";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/ContentType", method = RequestMethod.POST,
headers = "Content-Type=application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
public String request1(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//①得到请求的内容区数据的类型
String contentType = request.getContentType();
System.out.println("========ContentType:" + contentType);
//②得到请求的内容区数据的编码方式,如果请求中没有指定则为null
//注意,我们的CharacterEncodingFilter这个过滤器设置了编码(UTF-8)
//编码只能被指定一次,即如果客户端设置了编码,则过滤器不会再设置
String characterEncoding = request.getCharacterEncoding();
System.out.println("========CharacterEncoding:" + characterEncoding);
//③表示请求的内容区数据为form表单提交的参数,此时我们可以通过request.getParameter得到数据(key=value)
System.out.println(request.getParameter("realname"));
System.out.println(request.getParameter("username"));
return "success";
}
showForm功能处理方式:展示表单,且form的enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded",在提交时请求的内容类型头为“Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded”;
request1功能处理方法:只对请求头为“Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded”的请求进行处理(即消费请求内容区数据);
request.getContentType():可以得到请求头的内容区数据类型(即Content-Type头的值)
request.getCharacterEncoding():如“Content-Type:application/json;charset=GBK”,则得到的编码为“GBK”,否则如果你设置过滤器(CharacterEncodingFilter)则得到它设置的编码,否则返回null。
request.getParameter():因为请求的内容区数据为application/x-www-form-urlencoded格式的数据,因此我们可以通过request.getParameter()得到相应参数数据。
request中设置请求头“Content-Type:application/json;charset=GBK”表示请求的内容区数据为json类型数据,且内容区的数据以GBK进行编码;
(1、控制器cn.javass.chapter6.web.controller.consumesproduces.contenttype.RequestContentTypeController
@RequestMapping(value = "/request/ContentType", method = RequestMethod.POST,
headers = "Content-Type=application/json")
public String request2(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//①表示请求的内容区数据为json数据
InputStream is = request.getInputStream();
byte bytes[] = new byte[request.getContentLength()];
is.read(bytes);
//②得到请求中的内容区数据(以CharacterEncoding解码)
//此处得到数据后你可以通过如json-lib转换为其他对象
String jsonStr = new String(bytes, request.getCharacterEncoding());
System.out.println("json data:" + jsonStr);
return "success";
}
request2功能处理方法:只对请求头为“Content-Type:application/json”的进行请求处理(即消费请求内容区数据);
request.getContentLength():可以得到请求头的内容区数据的长度;
request.getCharacterEncoding():如“Content-Type:application/json;charset=GBK”,则得到的编码为“GBK”,否则如果你设置过滤器(CharacterEncodingFilter)则得到它设置的编码,否则返回null。
我们得到json的字符串形式后就能很简单的转换为JSON相关的对象。
(2、客户端发送json数据请求
//请求的地址
String url = "http://localhost:9080/springmvc-chapter6/request/ContentType";
//①创建Http Request(内部使用HttpURLConnection)
ClientHttpRequest request =
new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory().
createRequest(new URI(url), HttpMethod.POST);
//②设置请求头的内容类型头和内容编码(GBK)
request.getHeaders().set("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=gbk");
//③以GBK编码写出请求内容体
String jsonData = "{\"username\":\"zhang\", \"password\":\"123\"}";
request.getBody().write(jsonData.getBytes("gbk"));
//④发送请求并得到响应
ClientHttpResponse response = request.execute();
System.out.println(response.getStatusCode());
此处我们使用Spring提供的Http客户端API SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory创建了请求并设置了请求的Content-Type和编码并在响应体中写回了json数据(即生产json类型的数据),此处是硬编码,实际工作可以使用json-lib等工具进行转换。
具体代码在cn.javass.chapter6.web.controller.consumesproduces.contenttype.RequestContentTypeClient。
2.2、响应头的内容类型,表示发送到客户端的内容数据类型,和请求头的内容类型类似,只是方向相反。
@RequestMapping("/response/ContentType")
public void response1(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//①表示响应的内容区数据的媒体类型为html格式,且编码为utf-8(客户端应该以utf-8解码)
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//②写出响应体内容
response.getWriter().write("<font style='color:red'>hello</font>");
}
<!--[endif]-->
如上所示,通过response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8") 告诉客户端响应体媒体类型为html,编码为utf-8,大家可以通过chrome工具查看响应头为“Content-Type:text/html;charset=utf-8”,还一个“Content-Length:36”表示响应体大小。
代码在cn.javass.chapter6.web.controller.consumesproduces.contenttype.ResponseContentTypeController。
如上代码可以看出Content-Type可以指定请求/响应的内容体的媒体格式和可选的编码方式。如图6-9
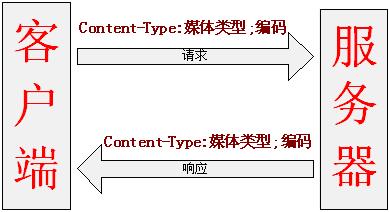
①客户端—发送请求—服务器:客户端通过请求头Content-Type指定内容体的媒体类型(即客户端此时是生产者),服务器根据Content-Type消费内容体数据(即服务器此时是消费者);
②服务器—发送请求—客户端:服务器生产响应头Content-Type指定的响应体数据(即服务器此时是生产者),客户端根据Content-Type消费内容体数据(即客户端此时是消费者)。
问题:
①服务器端可以通过指定【headers = "Content-Type=application/json"】来声明可处理(可消费)的媒体类型,即只消费Content-Type指定的请求内容体数据;
②客户端如何告诉服务器端它只消费什么媒体类型的数据呢?即客户端接受(需要)什么类型的数据呢?服务器应该生产什么类型的数据?此时我们可以请求的Accept请求头来实现这个功能。
三、Accept:用来指定什么媒体类型的响应是可接受的,即告诉服务器我需要什么媒体类型的数据,此时服务器应该根据Accept请求头生产指定媒体类型的数据。
2.1、json数据
(1、服务器端控制器
@RequestMapping(value = "/response/ContentType", headers = "Accept=application/json")
public void response2(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//①表示响应的内容区数据的媒体类型为json格式,且编码为utf-8(客户端应该以utf-8解码)
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
//②写出响应体内容
String jsonData = "{\"username\":\"zhang\", \"password\":\"123\"}";
response.getWriter().write(jsonData);
}
服务器根据请求头“Accept=application/json”生产json数据。
(2、客户端端接收服务器端json数据响应
使用浏览器测试(Ajax场景使用该方式)
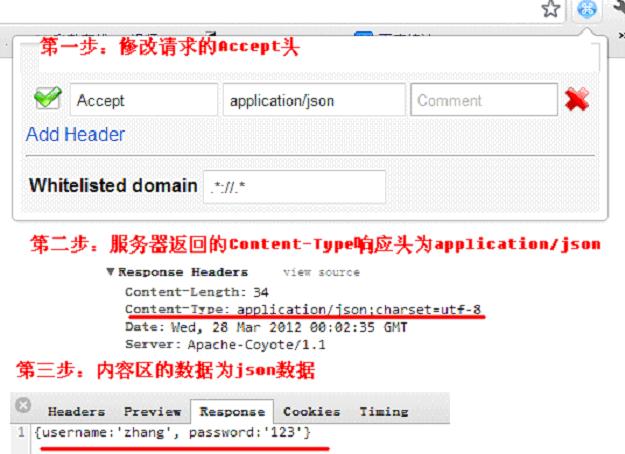
大家可以下载chrome的JSONView插件来以更好看的方式查看json数据,安装地址:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/chklaanhfefbnpoihckbnefhakgolnmc
使用普通客户端测试(服务器之间通信可使用该方式)
private static void jsonRequest() throws IOException, URISyntaxException {
//请求的地址
String url = "http://localhost:9080/springmvc-chapter6/response/ContentType";
//①创建Http Request(内部使用HttpURLConnection)
ClientHttpRequest request =
new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory().
createRequest(new URI(url), HttpMethod.POST);
//②设置客户端可接受的媒体类型(即需要什么类型的响应体数据)
request.getHeaders().set("Accept", "application/json");
//③发送请求并得到响应
ClientHttpResponse response = request.execute();
//④得到响应体的编码方式
Charset charset = response.getHeaders().getContentType().getCharSet();
//⑤得到响应体的内容
InputStream is = response.getBody();
byte bytes[] = new byte[(int)response.getHeaders().getContentLength()];
is.read(bytes);
String jsonData = new String(bytes, charset);
System.out.println("charset : " + charset + ", json data : " + jsonData);
}
request.getHeaders().set("Accept", "application/json"):表示客户端只接受(即只消费)json格式的响应数据;
response.getHeaders():可以得到响应头,从而可以得到响应体的内容类型和编码、内容长度。
2.2、xml数据
(1、服务器端控制器
@RequestMapping(value = "/response/ContentType", headers = "Accept=application/xml")
public void response3(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//①表示响应的内容区数据的媒体类型为xml格式,且编码为utf-8(客户端应该以utf-8解码)
response.setContentType("application/xml;charset=utf-8");
//②写出响应体内容
String xmlData = "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>";
xmlData += "<user><username>zhang</username><password>123</password></user>";
response.getWriter().write(xmlData);
}
和生产json数据唯一不同的两点:请求头为“Accept=application/xml”,响应体数据为xml。
(2、客户端端接收服务器端xml数据响应
使用浏览器测试(Ajax场景使用该方式)
使用普通客户端测试(服务器之间通信可使用该方式)
private static void xmlRequest() throws IOException, URISyntaxException {
//请求的地址
String url = "http://localhost:9080/springmvc-chapter6/response/ContentType";
//①创建Http Request(内部使用HttpURLConnection)
ClientHttpRequest request =
new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory().
createRequest(new URI(url), HttpMethod.POST);
//②设置客户端可接受的媒体类型(即需要什么类型的响应体数据)
request.getHeaders().set("Accept", "application/xml");
//③发送请求并得到响应
ClientHttpResponse response = request.execute();
//④得到响应体的编码方式
Charset charset = response.getHeaders().getContentType().getCharSet();
//⑤得到响应体的内容
InputStream is = response.getBody();
byte bytes[] = new byte[(int)response.getHeaders().getContentLength()];
is.read(bytes);
String xmlData = new String(bytes, charset);
System.out.println("charset : " + charset + ", xml data : " + xmlData);
}
request.getHeaders().set("Accept", "application/xml"):表示客户端只接受(即只消费)xml格式的响应数据;
response.getHeaders():可以得到响应头,从而可以得到响应体的内容类型和编码、内容长度。
许多开放平台,都提供了同一种数据的多种不同的表现形式,此时我们可以根据Accept请求头告诉它们我们需要什么类型的数据,他们根据我们的Accept来判断需要返回什么类型的数据。
实际项目使用Accept请求头是比较麻烦的,现在大多数开放平台(国内的新浪微博、淘宝、腾讯等开放平台)使用如下两种方式:
扩展名:如response/ContentType.json response/ContentType.xml方式,使用扩展名表示需要什么类型的数据;
参数:如response/ContentType?format=json response/ContentType?format=xml,使用参数表示需要什么类型的数据;
也就是说,目前我们可以使用如上三种方式实现来告诉服务器我们需要什么类型的数据,但麻烦的是现在有三种实现方式,难道我们为了支持三种类型的数据就要分别进行三种实现吗?当然不要这么麻烦,后续我们会学ContentNegotiatingViewResolver,它能帮助我们做到这一点。
6.6.5.2、生产者消费者流程图
生产者消费者流程,如图6-10:
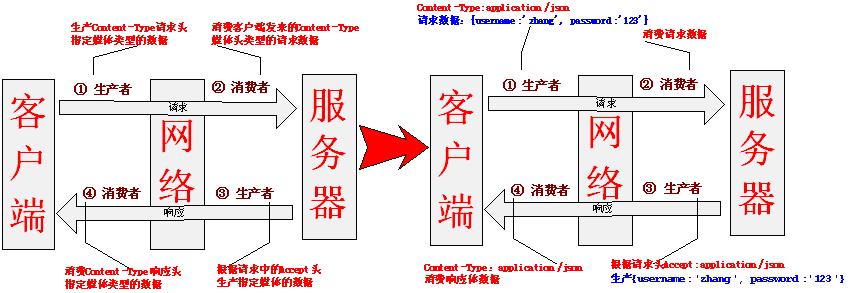
从图6-10可以看出:
请求阶段:客户端是生产者【生产Content-Type媒体类型的请求内容区数据】,服务器是消费者【消费客户端生产的Content-Type媒体类型的请求内容区数据】;
响应阶段:服务器是生产者【生产客户端请求头参数Accept指定的响应体数据】,客户端是消费者【消费服务器根据Accept请求头生产的响应体数据】。
如上生产者/消费者写法无法很好的体现我们分析的生产者/消费者模式,Spring3.1为生产者/消费者模式提供了简化支持,接下来我们学习一下如何在Spring3.1中来实现生产者/消费者模式吧。
6.6.5.3、生产者、消费者限定
Spring3.1开始支持消费者、生产者限定,而且必须使用如下HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter才支持:
<!--Spring3.1开始的注解 HandlerMapping -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"/>
<!--Spring3.1开始的注解 HandlerAdapter -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"/>
一、功能处理方法是消费者
@RequestMapping(value = "/consumes", consumes = {"application/json"}):此处使用consumes来指定功能处理方法能消费的媒体类型,其通过请求头的“Content-Type”来判断。
此种方式相对使用@RequestMapping的“headers = "Content-Type=application/json"”更能表明你的目的。
服务器控制器代码详解cn.javass.chapter6.web.controller.consumesproduces.ConsumesController;
客户端代码类似于之前的Content-Type中的客户端,详见ConsumesClient.。
二、功能处理方法是生产者
@RequestMapping(value = "/produces", produces = "application/json"):表示将功能处理方法将生产json格式的数据,此时根据请求头中的Accept进行匹配,如请求头“Accept:application/json”时即可匹配;
@RequestMapping(value = "/produces", produces = "application/xml"):表示将功能处理方法将生产xml格式的数据,此时根据请求头中的Accept进行匹配,如请求头“Accept:application/xml”时即可匹配。
此种方式相对使用@RequestMapping的“headers = "Accept=application/json"”更能表明你的目的。
服务器控制器代码详解cn.javass.chapter6.web.controller.consumesproduces.ProducesController;
客户端代码类似于之前的Content-Type中的客户端,详见ProducesController.。
当你有如下Accept头:
①Accept:text/html,application/xml,application/json
将按照如下顺序进行produces的匹配 ①text/html ②application/xml ③application/json
②Accept:application/xml;q=0.5,application/json;q=0.9,text/html
将按照如下顺序进行produces的匹配 ①text/html ②application/json ③application/xml
q参数为媒体类型的质量因子,越大则优先权越高(从0到1)
③Accept:/,text/*,text/html
将按照如下顺序进行produces的匹配 ①text/html ②text/ ③/*
即匹配规则为:最明确的优先匹配。
代码详见ProducesPrecedenceController1、ProducesPrecedenceController2、ProducesPrecedenceController3。
Accept详细信息,请参考http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2616#section-14.1。
三、窄化时是覆盖 而 非继承
如类级别的映射为 @RequestMapping(value="/narrow", produces="text/html"),方法级别的为@RequestMapping(produces="application/xml"),此时方法级别的映射将覆盖类级别的,因此请求头“Accept:application/xml”是成功的,而“text/html”将报406错误码,表示不支持的请求媒体类型。
详见cn.javass.chapter6.web.controller.consumesproduces.NarrowController。
只有生产者/消费者 模式 是 覆盖,其他的使用方法是继承,如headers、params等都是继承。
四、组合使用是“或”的关系
@RequestMapping(produces={"text/html", "application/json"}) :将匹配“Accept:text/html”或“Accept:application/json”。
五、问题
消费的数据,如JSON数据、XML数据都是由我们读取请求的InputStream并根据需要自己转换为相应的模型数据,比较麻烦;
生产的数据,如JSON数据、XML数据都是由我们自己先把模型数据转换为json/xml等数据,然后输出响应流,也是比较麻烦的。
Spring提供了一组注解(@RequestBody、@ResponseBody)和一组转换类(HttpMessageConverter)来完成我们遇到的问题,详见6.6.8节。