作为系列文章的第四篇,本篇主要介绍 Flutter 中 Redux 的使用,并结合Redux 完成实时的主题切换与多语言切换功能。
前文:
Flutter 作为响应式框架,通过 state 实现跨帧渲染的逻辑,难免让人与 React 和 React Native 联系起来,而其中 React 下“广为人知”的 Redux 状态管理,其实在 Flutter 中同样适用。
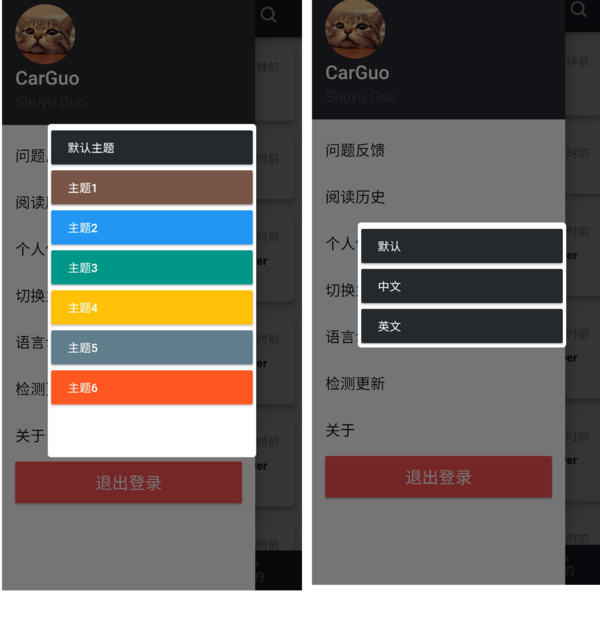
我们最终将实现如下图的效果,相应代码在 GSYGithubAppFlutter 中可找到,本篇 Flutter 中所使用的 Redux 库是 flutter_redux 。
一、Redux
Redux 的概念是状态管理,那在已有 state 的基础上,为什么还需要 Redux ?
因为使用 Redux 的好处是:共享状态和单一数据。
试想一下,App内有多个地方使用到登陆用户的数据,这时候如果某处对用户数据做了修改,各个页面的同步更新会是一件麻烦的事情。
但是引入 Redux 后,某个页面修改了当前用户信息,所有绑定了 Redux 的控件,将由 Redux 自动同步刷新。See!这在一定程度节省了我们的工作量,并且单一数据源在某些场景下也方便管理。同理我们后面所说的 主题 和 多语言 切换也是如此。
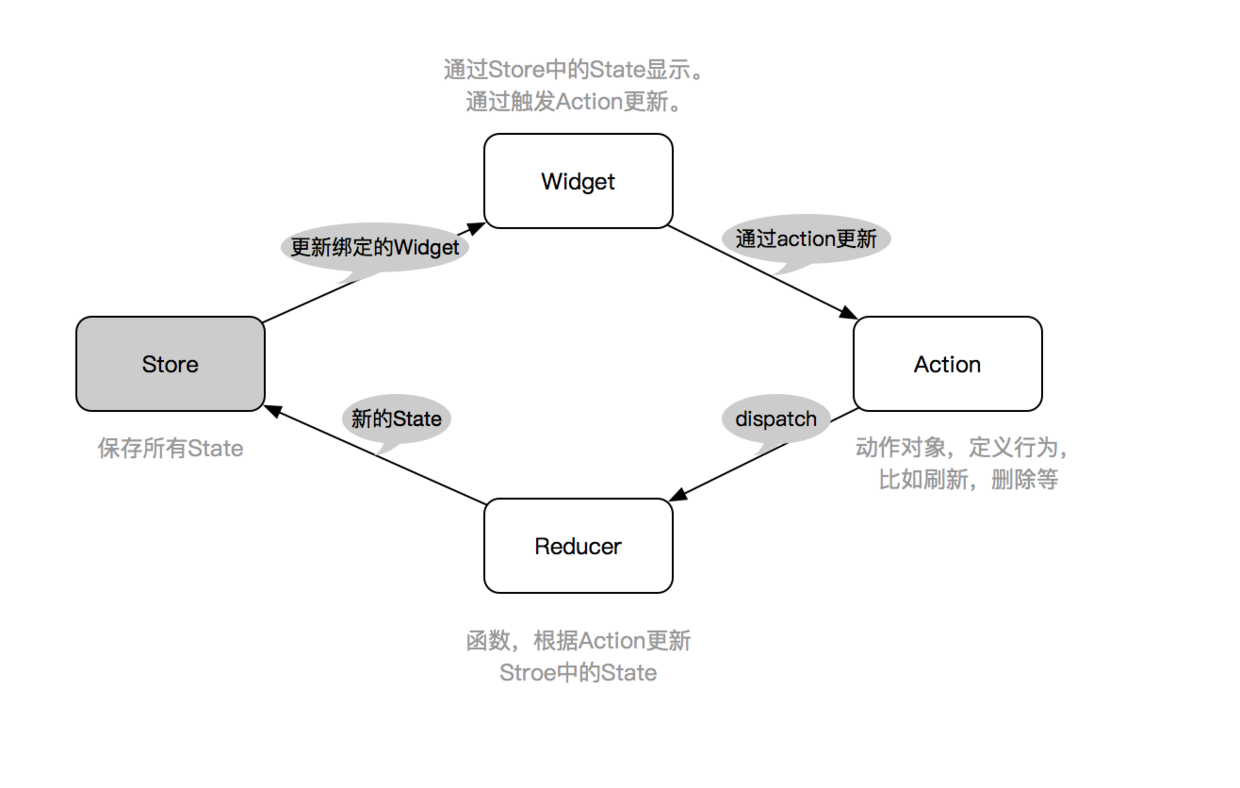
如上图,Redux 的主要由三部分组成:Store 、Action 、 Reducer 。
- Action 用于定义一个数据变化的请求行为。
- Reducer 用于根据 Action 产生新状态,一般是一个方法。
- Store 用于存储和管理 state。
所以一般流程为:
1、Widget 绑定了 Store 中的 state 数据。
2、Widget 通过 Action 发布一个动作。
3、Reducer 根据 Action 更新 state。
4、更新 Store 中 state 绑定的 Widget。
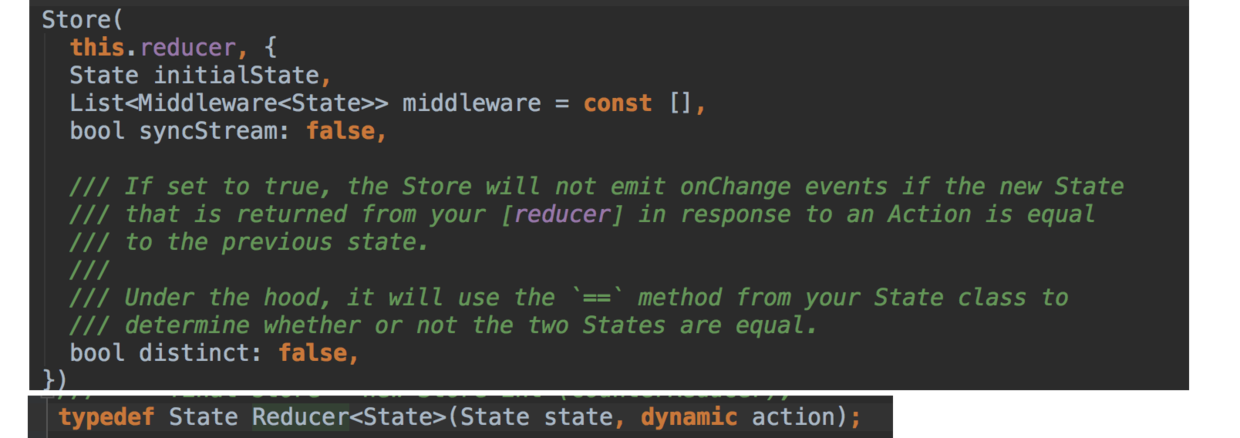
根据这个流程,首先我们要创建一个 Store 。
如下图,创建 Store 需要 reducer ,而 reducer 实际上是一个带有 state 和 action 的方法,并返回新的 State 。
所以我们需要先创建一个 State 对象 GSYState 类,用于储存需要共享的数据。比如下方代码的: 用户信息、主题、语言环境 等。
接着我们需要定义 Reducer 方法 appReducer :将 GSYState 内的每一个参数,和对应的 action 绑定起来,返回完整的 GSYState 。这样我们就确定了 State 和 Reducer 用于创建 Store。
///全局Redux store 的对象,保存State数据
class GSYState {
///用户信息
User userInfo;
///主题
ThemeData themeData;
///语言
Locale locale;
///构造方法
GSYState({this.userInfo, this.themeData, this.locale});
}
///创建 Reducer
///源码中 Reducer 是一个方法 typedef State Reducer<State>(State state, dynamic action);
///我们自定义了 appReducer 用于创建 store
GSYState appReducer(GSYState state, action) {
return GSYState(
///通过自定义 UserReducer 将 GSYState 内的 userInfo 和 action 关联在一起
userInfo: UserReducer(state.userInfo, action),
///通过自定义 ThemeDataReducer 将 GSYState 内的 themeData 和 action 关联在一起
themeData: ThemeDataReducer(state.themeData, action),
///通过自定义 LocaleReducer 将 GSYState 内的 locale 和 action 关联在一起
locale: LocaleReducer(state.locale, action),
);
}
如上代码,GSYState 的每一个参数,是通过独立的自定义 Reducer 返回的。比如 themeData 是通过 ThemeDataReducer 方法产生的,ThemeDataReducer 其实是将 ThemeData 和一系列 Theme 相关的 Action 绑定起来,用于和其他参数分开。这样就可以独立的维护和管理 GSYState 中的每一个参数。
继续上面流程,如下代码所示,通过 flutter_redux 的 combineReducers 与 TypedReducer,将 RefreshThemeDataAction 类 和 _refresh 方法绑定起来,最终会返回一个 ThemeData 实例。也就是说:用户每次发出一个 RefreshThemeDataAction ,最终都会触发 _refresh 方法,然后更新 GSYState 中的 themeData。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:redux/redux.dart';
///通过 flutter_redux 的 combineReducers,创建 Reducer<State>
final ThemeDataReducer = combineReducers<ThemeData>([
///将Action,处理Action动作的方法,State绑定
TypedReducer<ThemeData, RefreshThemeDataAction>(_refresh),
]);
///定义处理 Action 行为的方法,返回新的 State
ThemeData _refresh(ThemeData themeData, action) {
themeData = action.themeData;
return themeData;
}
///定义一个 Action 类
///将该 Action 在 Reducer 中与处理该Action的方法绑定
class RefreshThemeDataAction {
final ThemeData themeData;
RefreshThemeDataAction(this.themeData);
}
OK,现在我们可以愉悦的创建 Store 了。如下代码所示,在创建 Store 的同时,我们通过 initialState 对 GSYState 进行了初始化,然后通过 StoreProvider 加载了 Store 并且包裹了 MaterialApp 。 至此我们完成了 Redux 中的初始化构建。
void main() {
runApp(new FlutterReduxApp());
}
class FlutterReduxApp extends StatelessWidget {
/// 创建Store,引用 GSYState 中的 appReducer 创建 Reducer
/// initialState 初始化 State
final store = new Store<GSYState>(
appReducer,
initialState: new GSYState(
userInfo: User.empty(),
themeData: new ThemeData(
primarySwatch: GSYColors.primarySwatch,
),
locale: Locale('zh', 'CH')),
);
FlutterReduxApp({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
/// 通过 StoreProvider 应用 store
return new StoreProvider(
store: store,
child: new MaterialApp(),
);
}
}
And then,接下来就是使用了。如下代码所示,通过在 build 中使用 StoreConnector ,通过 converter 转化 store.state 的数据,最后通过 builder 返回实际需要渲染的控件,这样就完成了数据和控件的绑定。当然,你也可以使用StoreBuilder 。
class DemoUseStorePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
///通过 StoreConnector 关联 GSYState 中的 User
return new StoreConnector<GSYState, User>(
///通过 converter 将 GSYState 中的 userInfo返回
converter: (store) => store.state.userInfo,
///在 userInfo 中返回实际渲染的控件
builder: (context, userInfo) {
return new Text(
userInfo.name,
);
},
);
}
}
最后,当你需要触发更新的时候,只需要如下代码即可。
StoreProvider.of(context).dispatch(new UpdateUserAction(newUserInfo));
So,或者简单的业务逻辑下,Redux 并没有什么优势,甚至显得繁琐。但是一旦框架搭起来,在复杂的业务逻辑下就会显示格外愉悦了。
二、主题
Flutter 中官方默认就支持主题设置,MaterialApp 提供了 theme 参数设置主题,之后可以通过 Theme.of(context) 获取到当前的 ThemeData 用于设置控件的颜色字体等。
ThemeData 的创建提供很多参数,这里主要说 primarySwatch 参数。 primarySwatch 是一个 MaterialColor 对象,内部由10种不同深浅的颜色组成,用来做主题色调再合适不过。
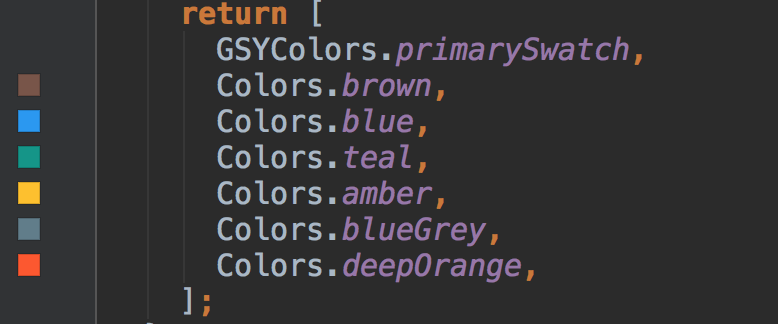
如下图和代码所示,Flutter 默认提供了很多主题色,同时我们也可以通过 MaterialColor 实现自定义的主题色。
MaterialColor primarySwatch = const MaterialColor(
primaryValue,
const <int, Color>{
50: const Color(primaryLightValue),
100: const Color(primaryLightValue),
200: const Color(primaryLightValue),
300: const Color(primaryLightValue),
400: const Color(primaryLightValue),
500: const Color(primaryValue),
600: const Color(primaryDarkValue),
700: const Color(primaryDarkValue),
800: const Color(primaryDarkValue),
900: const Color(primaryDarkValue),
},
);
那如何实现实时的主题切换呢?当然是通过 Redux 啦!
前面我们已经在 GSYState 中创建了 themeData ,此时将它设置给 MaterialApp 的 theme 参数,之后我们通过 dispatch 改变 themeData 即可实现主题切换。
注意,因为你的 MaterialApp 也是一个 StatefulWidget ,如下代码所示,还需要利用 StoreBuilder 包裹起来,之后我们就可以通过 dispatch 修改主题,通过 Theme.of(context).primaryColor 获取主题色啦。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
/// 通过 StoreProvider 应用 store
return new StoreProvider(
store: store,
child: new StoreBuilder<GSYState>(builder: (context, store) {
return new MaterialApp(
theme: store.state.themeData);
}),
);
}
····
ThemeData themeData = new ThemeData(primarySwatch: colors[index]);
store.dispatch(new RefreshThemeDataAction(themeData));
三、国际化
Flutter的国际化按照官网文件 internationalization 看起来稍微有些复杂,也没有提及实时切换,所以这里介绍下快速的实现。当然,少不了 Redux !
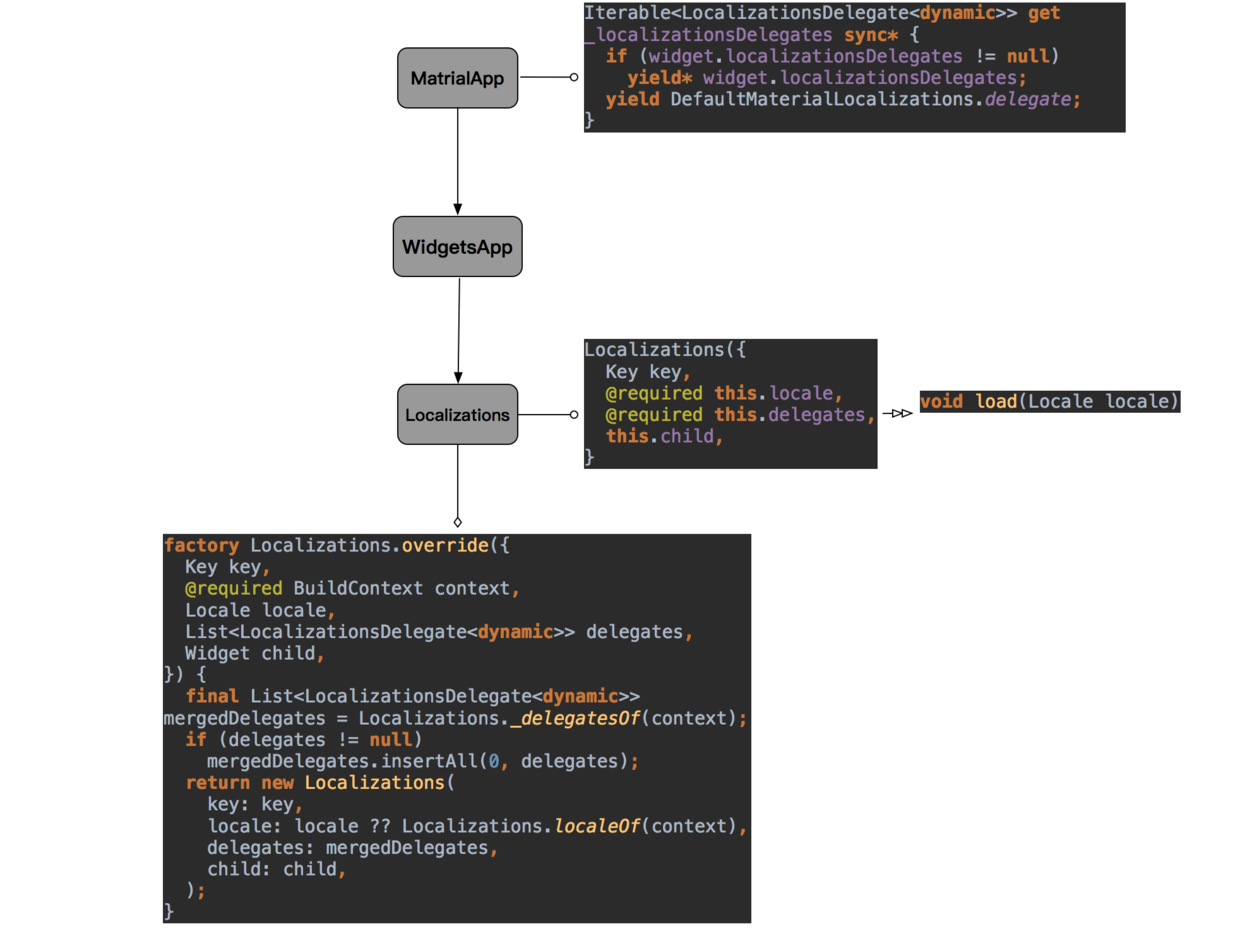
如上图所示大致流程,同样是通过默认 MaterialApp 设置,自定义的多语言需要实现的是: LocalizationsDelegate 和 Localizations。最终流程会通过 Localizations 使用 Locale 加载这个 delegate。所以我们要做的是:
- 实现 LocalizationsDelegate。
- 实现 Localizations。
- 通过 Store 的 Locale 切换语言。
如下代码所示,创建自定义 delegate 需要继承 LocalizationsDelegate 对象,其中主要实现 load 方法。我们可以是通过方法的 locale 参数,判断需要加载的语言,然后返回我们自定义好多语言实现类 GSYLocalizations ,最后通过静态 delegate 对外提供 LocalizationsDelegate。
/**
* 多语言代理
* Created by guoshuyu
* Date: 2018-08-15
*/
class GSYLocalizationsDelegate extends LocalizationsDelegate<GSYLocalizations> {
GSYLocalizationsDelegate();
@override
bool isSupported(Locale locale) {
///支持中文和英语
return ['en', 'zh'].contains(locale.languageCode);
}
///根据locale,创建一个对象用于提供当前locale下的文本显示
@override
Future<GSYLocalizations> load(Locale locale) {
return new SynchronousFuture<GSYLocalizations>(new GSYLocalizations(locale));
}
@override
bool shouldReload(LocalizationsDelegate<GSYLocalizations> old) {
return false;
}
///全局静态的代理
static GSYLocalizationsDelegate delegate = new GSYLocalizationsDelegate();
}
上面提到的 GSYLocalizations 其实是一个自定义对象,如下代码所示,它会根据创建时的 Locale ,通过 locale.languageCode 判断返回对应的语言实体:GSYStringBase的实现类。
因为 GSYLocalizations 对象最后会通过Localizations 加载,所以 Locale 也是在那时,通过 delegate 赋予。同时在该 context 下,可以通过Localizations.of 获取 GSYLocalizations,比如: GSYLocalizations.of(context).currentLocalized.app_name。
///自定义多语言实现
class GSYLocalizations {
final Locale locale;
GSYLocalizations(this.locale);
///根据不同 locale.languageCode 加载不同语言对应
///GSYStringEn和GSYStringZh都继承了GSYStringBase
static Map<String, GSYStringBase> _localizedValues = {
'en': new GSYStringEn(),
'zh': new GSYStringZh(),
};
GSYStringBase get currentLocalized {
return _localizedValues[locale.languageCode];
}
///通过 Localizations 加载当前的 GSYLocalizations
///获取对应的 GSYStringBase
static GSYLocalizations of(BuildContext context) {
return Localizations.of(context, GSYLocalizations);
}
}
///语言实体基类
abstract class GSYStringBase {
String app_name;
}
///语言实体实现类
class GSYStringEn extends GSYStringBase {
@override
String app_name = "GSYGithubAppFlutter";
}
///使用
GSYLocalizations.of(context).currentLocalized.app_name
说完了 delegate , 接下来就是 Localizations 了。在上面的流程图中可以看到, Localizations 提供一个 override 方法构建 Localizations ,这个方法中可以设置 locale,而我们需要的正是实时的动态切换语言显示。
如下代码,我们创建一个 GSYLocalizations 的 Widget,通过 StoreBuilder 绑定 Store,然后通过 Localizations.override 包裹我们需要构建的页面,将 Store 中的 locale 和 Localizations 的 locale 绑定起来。
class GSYLocalizations extends StatefulWidget {
final Widget child;
GSYLocalizations({Key key, this.child}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<GSYLocalizations> createState() {
return new _GSYLocalizations();
}
}
class _GSYLocalizations extends State<GSYLocalizations> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new StoreBuilder<GSYState>(builder: (context, store) {
///通过 StoreBuilder 和 Localizations 实现实时多语言切换
return new Localizations.override(
context: context,
locale: store.state.locale,
child: widget.child,
);
});
}
}
如下代码,最后将 GSYLocalizations 使用到 MaterialApp 中。通过 store.dispatch 切换 Locale 即可。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
/// 通过 StoreProvider 应用 store
return new StoreProvider(
store: store,
child: new StoreBuilder<GSYState>(builder: (context, store) {
return new MaterialApp(
///多语言实现代理
localizationsDelegates: [
GlobalMaterialLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalWidgetsLocalizations.delegate,
GSYLocalizationsDelegate.delegate,
],
locale: store.state.locale,
supportedLocales: [store.state.locale],
routes: {
HomePage.sName: (context) {
///通过 Localizations.override 包裹一层。---这里
return new GSYLocalizations(
child: new HomePage(),
);
},
});
}),
);
}
///切换主题
static changeLocale(Store<GSYState> store, int index) {
Locale locale = store.state.platformLocale;
switch (index) {
case 1:
locale = Locale('zh', 'CH');
break;
case 2:
locale = Locale('en', 'US');
break;
}
store.dispatch(RefreshLocaleAction(locale));
}
最后的最后,在改变时记录状态,在启动时取出后dispatch,至此主题和多语言设置完成。
自此,第四篇终于结束了!(///▽///)
资源推荐
完整开源项目推荐:
文章
《Flutter完整开发实战详解(一、Dart语言和Flutter基础)》