React Router 入门实战教学

前言
若你是从一开始一路走到这里读者请先给自己一个爱的鼓励吧!在经历了 React 基础的训练后,相信各位读者应该都等不及想大展拳脚了!接下来我们将进行比较复杂的应用程序开发并和读者介绍目前市场上常见的不刷页单页式应用程序(single page application)的设计方式。
单页式应用程序(single page application)
传统的 Web 开发主要是由伺服器管理 URL Routing 和渲染 HTML 页面,过往每次 URL 一换或使用者连接一点,就需要重新从伺服器端重新载入页面。但随著使用者对于使用者体验的要求提升,许多的网页应用程序纷纷设计成不刷页的单页式应用程序(single page application),由前端负责 URL 的 routing 管理,若需要和后端进行 API 资料沟通的话,通常也会使用 Ajax 的技术。在 React 开发世界中主流是使用 react-router 这个 routing 管理用的 library。
React Router 环境设置
先透过以下指令在根目录产生 npm 配置文件 package.json :
$ npm init
安装相关包(包含开发环境使用的包):
$ npm install --save react react-dom react-router
$ npm install --save-dev babel-core babel-eslint babel-loader babel-preset-es2015 babel-preset-react eslint eslint-config-airbnb eslint-loader eslint-plugin-import eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y eslint-plugin-react webpack webpack-dev-server html-webpack-plugin
安装好后我们可以设计一下我们的文件夹结构,首先我们在根目录建立 src 和 res 文件夹,分别放置 script 的 source 和静态资源(如:全域使用的 .css 和图档)。在 components 文件夹中我们会放置所有 components(个别组件文件夹中会用 index.js 输出组件,让引入组件更简洁),其余配置文件则放置于根目录下。
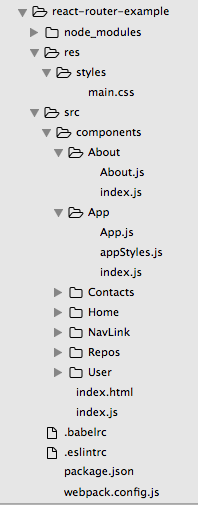
接下来我们先设定一下开发文档。
设定 Babel 的配置文件:
.babelrc{ "presets": [ "es2015", "react", ], "plugins": [] }设定 ESLint 的配置文件和规则:
.eslintrc{ "extends": "airbnb", "rules": { "react/jsx-filename-extension": [1, { "extensions": [".js", ".jsx"] }], }, "env" :{ "browser": true, } }设定 Webpack 配置文件:
webpack.config.js// 让你可以动态插入 bundle 好的 .js 档到 .index.html const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin'); const HTMLWebpackPluginConfig = new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: `${__dirname}/src/index.html`, filename: 'index.html', inject: 'body', }); // entry 为进入点,output 为进行完 eslint、babel loader 转译后的档案位置 module.exports = { entry: [ './src/index.js', ], output: { path: `${__dirname}/dist`, filename: 'index_bundle.js', }, module: { preLoaders: [ { test: /\.jsx$|\.js$/, loader: 'eslint-loader', include: `${__dirname}/src`, exclude: /bundle\.js$/ } ], loaders: [{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: 'babel-loader', query: { presets: ['es2015', 'react'], }, }], }, // 启动开发测试用 server 设定(不能用在 production) devServer: { inline: true, port: 8008, }, plugins: [HTMLWebpackPluginConfig], };
太好了!这样我们就完成了开发环境的设定可以开始动手实践 React Router 应用程序了!
开始 React Routing 之旅
HTML Markup:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ReactRouter</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="../res/styles/main.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
</html>
以下是 webpack.config.js 的进入点 src/index.js,负责管理 Router 和 render 组件。这边我们要先详细讨论的是,为了使用 React Router 功能引入了许多 react-router 内部的组件。
Router
Router是放置 Route 的容器,其本身不定义 routing ,真正 routing 规则由Route定义。Route
Route负责 URL 和对应的组件关系,可以有多个Route规则也可以有嵌套(nested)Routing。像下面的例子就是每个页面都会先载入App组件再载入对应 URL 的组件。history
Router中有一个属性history的规则,这边使用我们使用hashHistory,使用 routing 将由hash(#)变化决定。例如:当使用者拜访http://www.github.com/,实际看到的会是http://www.github.com/#/。下列范例若是拜访了/about则会看到http://localhost:8008/#/about并载入App组件再载入About组件。hashHistory 教学范例使用的,会通过
hash进行对应。好处是简单易用,不用多余设定。browserHistory 适用于伺服器端渲染,但需要设定伺服器端避免处理错误,这部份我们会在后面的章节详细说明。注意的是若是使用 Webpack 开发用伺服器需加上
--history-api-fallback$ webpack-dev-server --inline --content-base . --history-api-fallbackcreateMemoryHistory 主要用于伺服器渲染,使用上会建立一个存在记忆体的
history物件,不会修改浏览器的网址位置。const history = createMemoryHistory(location)
path
path是对应 URL 的规则。例如:/repos/torvalds会对应到/repos/:name的位置,并将参数传入Repos组件中。由this.props.params.name取得参数。顺带一提,若为查询参数/user?q=torvalds则由this.props.location.query.q取得参数。IndexRoute 由于
/情况下 App 组件对应的this.props.children会是undefinded,所以使用IndexRoute来解决对应问题。这样当 URL 为/时将会对应到 Home 组件。不过要注意的是IndexRoute没有 path 属性。
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Router, Route, hashHistory, IndexRoute } from 'react-router';
import App from './components/App';
import Home from './components/Home';
import Repos from './components/Repos';
import About from './components/About';
import User from './components/User';
import Contacts from './components/Contacts';
ReactDOM.render(
<Router history={hashHistory}>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<IndexRoute component={Home} />
<Route path="/repos/:name" component={Repos} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/user" component={User} />
<Route path="/contacts" component={Contacts} />
</Route>
</Router>,
document.getElementById('app'));
/* 另外一种写法:
const routes = (
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<IndexRoute component={Home} />
<Route path="/repos/:name" component={Repos} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/user" component={User} />
<Route path="/contacts" component={Contacts} />
</Route>
);
ReactDOM.render(
<Router routes={routes} history={hashHistory} />,
document.getElementById('app'));
*/
由于我们在 index.js 使用嵌套 routing,把 App 组件当做每个组件都会载入的母模版,亦即进入每个对应页面载入对应组件前都会先载入 App 组件。这样就可以让每个页面都有导览列连接可以点选,同时可以透过 props.children 载入对应 URL 的子组件。
Link
Link组件主要用于点击后连接转换,可以想成是<a>超连接的 React 版本。若是希望当点击时候有对应的 css style,可以使用activeStyle、activeClassName去做设定。范例分别使用于index.html使用传统CSS载入、Inline Style、外部引入Inline Style写法。IndexLink IndexLink 主要是了处理
index用途,特别注意当 child routeactived时,parent route 也会actived。所以我们回首页的连接使用<IndexLink />内部的onlyActiveOnIndex属性来解决这个问题。Redirect、IndexRedirect 这边虽然没有用到,但若读者有需要使用到连接跳转的话可以参考这两个组件,用法类似于
Route和IndexRedirect。
以下是 src/components/App/App.js 完整代码:
import React from 'react';
import { Link, IndexLink } from 'react-router';
import styles from './appStyles';
import NavLink from '../NavLink';
const App = (props) => (
<div>
<h1>React Router Tutorial</h1>
<ul>
<li><IndexLink to="/" activeClassName="active">Home</IndexLink></li>
<li><Link to="/about" activeStyle={{ color: 'green' }}>About</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/repos/react-router" activeStyle={styles.active}>Repos</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/user" activeClassName="active">User</Link></li>
<li><NavLink to="/contacts">Contacts</NavLink></li>
</ul>
<!-- 我们将 App 组件当做每个组件都会载入的母模版,因此可以透过 children 载入对应 URL 的子组件 -->
{props.children}
</div>
);
App.propTypes = {
children: React.PropTypes.object,
};
export default App;
对应的组件内部使用 Functional Component 进行 UI 渲染:
以下是 src/components/Repos/Repos.js 完整代码:
import React from 'react';
const Repos = (props) => (
<div>
<h3>Repos</h3>
<h5>{props.params.name}</h5>
</div>
);
Repos.propTypes = {
params: React.PropTypes.object,
};
export default Repos;
详细的代码读者可以参考范例文件夹,若读者跟著范例完成的话,可以在终端机上执行 npm start,并于浏览器 http://localhost:8008看到以下成果,当你点选连接时会切换对应组件并改变 actived 状态!

总结
到这边我们又一起完成了一个重要的一关,学习 routing 对于使用 React 开发复杂应用程序是非常重要的一步,接下来我们将一起学习一个相对独立的单元 ImmutableJS,但学习 ImmutableJS 可以让我们在使用 React 和 Flux/Redux 可以有更好的性能和避免一些副作用。
延伸阅读
- Leveling Up With React: React Router
- Programmatically navigate using react router
- React Router 使用教程
- React Router 中文文档
- React Router Tutorial
(iamge via seanamarasinghe)
任意门
| 回首页 | 上一章:React Component 规格与生命周期(Life Cycle) | 下一章:ImmutableJS 入门教学 |
| 纠错、提问或许愿 |