9.1 NumPy
原文:NumPy
译者:飞龙
致谢:派生于 Olivier Grisel 分享的 scikit-learn 和 IPython 并行机器学习
- NumPy 数组,
dtype和形状 - 常见数组操作
- 原地修改形状和更新
- 合并数组
- 创建示例数据
import numpy as np
NumPy 数组,dtype和形状
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(a)
print(a.shape)
print(a.dtype)
'''
[1 2 3]
(3,)
int64
'''
b = np.array([[0, 2, 4], [1, 3, 5]])
print(b)
print(b.shape)
print(b.dtype)
'''
[[0 2 4]
[1 3 5]]
(2, 3)
int64
'''
np.zeros(5)
# array([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
np.ones(shape=(3, 4), dtype=np.int32)
'''
array([[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1]], dtype=int32)
'''
常见数组操作
c = b * 0.5
print(c)
print(c.shape)
print(c.dtype)
'''
[[ 0. 1. 2. ]
[ 0.5 1.5 2.5]]
(2, 3)
float64
'''
d = a + c
print(d)
'''
[[ 1. 3. 5. ]
[ 1.5 3.5 5.5]]
'''
d[0]
# array([ 1., 3., 5.])
d[0, 0]
# 1.0
d[:, 0]
# array([ 1. , 1.5])
d.sum()
# 19.5
d.mean()
# 3.25
d.sum(axis=0)
# array([ 2.5, 6.5, 10.5])
d.mean(axis=1)
# array([ 3. , 3.5])
原地修改形状和更新
e = np.arange(12)
print(e)
# [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
# f 是 e 的内容的视图
f = e.reshape(3, 4)
print(f)
'''
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
'''
# 将 e 从索引 5 开始的值设为 0
e[5:] = 0
print(e)
# [0 1 2 3 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
# f 也更新了
f
'''
array([[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]])
'''
# OWNDATA 展示了 f 并没有自己的数据
f.flags
'''
C_CONTIGUOUS : True
F_CONTIGUOUS : False
OWNDATA : False
WRITEABLE : True
ALIGNED : True
UPDATEIFCOPY : False
'''
合并数组
a
# array([1, 2, 3])
b
'''
array([[0, 2, 4],
[1, 3, 5]])
'''
d
'''
array([[ 1. , 3. , 5. ],
[ 1.5, 3.5, 5.5]])
'''
np.concatenate([a, a, a])
# array([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3])
# 广播在需要时自动完成
np.vstack([a, b, d])
'''
array([[ 1. , 2. , 3. ],
[ 0. , 2. , 4. ],
[ 1. , 3. , 5. ],
[ 1. , 3. , 5. ],
[ 1.5, 3.5, 5.5]])
'''
# 在机器学习中,使用 hstack
# 来扩充或者添加新的/交叉特征很有用
np.hstack([b, d])
'''
array([[ 0. , 2. , 4. , 1. , 3. , 5. ],
[ 1. , 3. , 5. , 1.5, 3.5, 5.5]])
'''
创建样例数据
%matplotlib inline
import pylab as plt
import seaborn
seaborn.set()
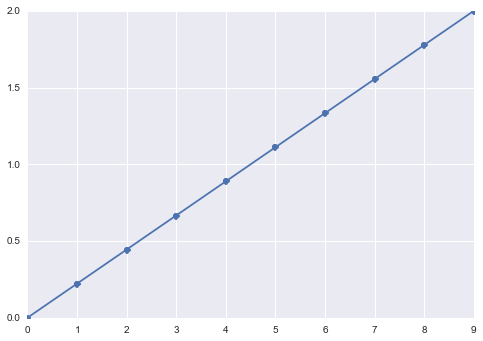
# 创建特定区间上的等间隔的数字
x = np.linspace(0, 2, 10)
plt.plot(x, 'o-');
plt.show()
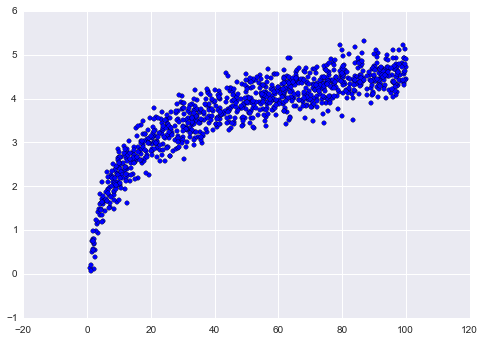
# 创建样例数据,添加一些噪声
x = np.random.uniform(1, 100, 1000)
y = np.log(x) + np.random.normal(0, .3, 1000)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()